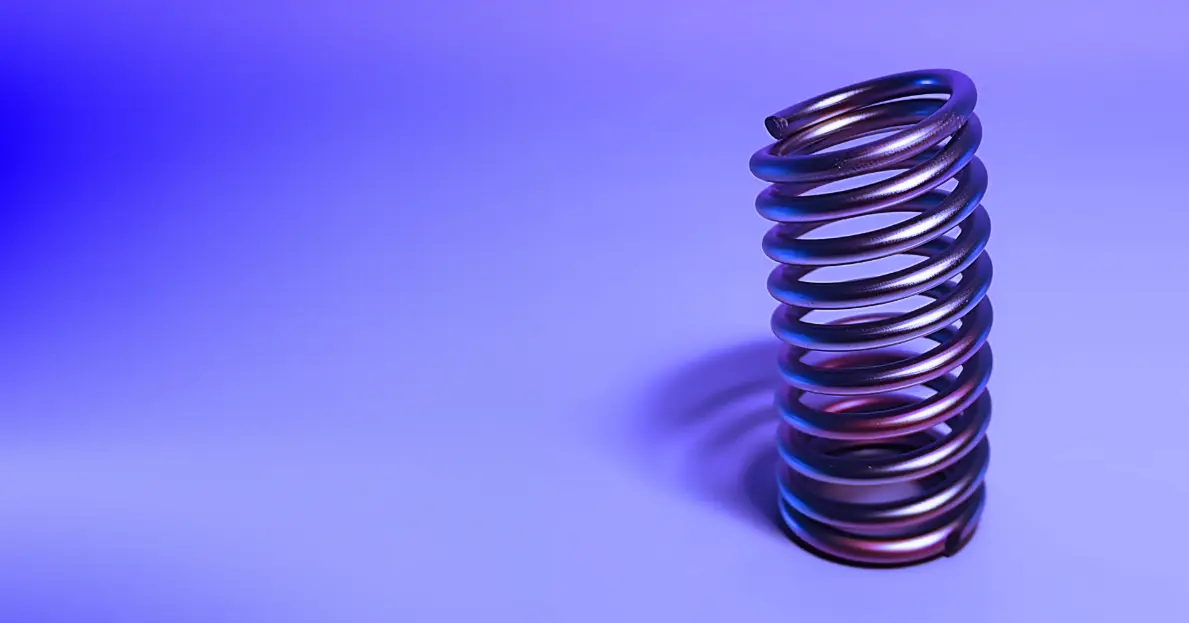
Antenna springs protect antennas from damage due to impact or harsh environmental conditions. This article will cover the different types of antenna springs, their features, and best practices for installation and maintenance. For example, while heavy-duty antenna springs are useful for vehicles in off-road conditions, lighter springs are suitable for stationary setups. By understanding the specific environment and requirements of your application, you can make informed decisions that enhance the safety and longevity of your antenna systems.
Understanding Antenna Springs- Definition and Functions
Antenna springs are flexible connectors placed between the antenna and its mounting base. Their main function is to absorb shock and prevent antenna damage caused by interactions with external forces such as wind or accidental contact with objects. By allowing the antenna to flex instead of break, these springs help preserve both the antenna and the connected equipment.
Antenna springs are used in mobile communications for devices like CB radios in vehicles and in static setups like base station antennas. They are designed to handle mechanical stress, thereby increasing the life and reliability of the antenna. For example, in mobile applications, when a vehicle passes under a low bridge or through dense foliage, the antenna flexes due to the spring, preventing damage and maintaining signal integrity.
Varieties of Antenna Springs and Their Unique Features
Heavy-Duty Antenna Springs: Designed for applications requiring high durability, such as off-road vehicles and trucks. These springs are made from materials like stainless steel, ensuring they can handle challenging conditions. For example, a heavy-duty spring is necessary for trucks frequently driven on rough terrain to prevent antenna damage from vibrations and impacts.
Light-Duty Antenna Springs: Suitable for standard passenger vehicles or light-duty communication setups. These are designed for everyday use where the risk of severe impact is lower. Using light-duty springs in off-road situations can lead to failure or reduced lifespan due to their inability to withstand repeated heavy impacts.
Short Antenna Springs: These springs are compact and provide moderate flexibility, often used in space-limited applications requiring some shock absorption. Due to their shorter length, they are less flexible than long springs but adequate for urban installations.
Long Antenna Springs: Offering greater flexibility and range of motion, these springs are suitable for environments with frequent impacts or movement, providing better protection. For example, in rural settings where vehicles encounter many obstacles, long springs help absorb shocks that could damage the antenna.
Coated Antenna Springs: Featuring a protective layer, these springs are designed to withstand harsh conditions, such as corrosion from salty air in coastal areas. The protective coating extends their longevity in corrosive environments, making them suitable for marine applications and seaside installations.
Installation, Maintenance, and Safety Measures
Installation:
- Ensure the antenna spring is compatible with the antenna and mount before installation. For example, a spring designed for a heavy-duty antenna may not function well with a smaller, lightweight antenna, leading to reduced performance.
- Tighten bolts and screws adequately to secure the spring, avoiding over-tightening which can strip threads. Stripped threads can cause the antenna to become loose over time, potentially leading to system failure.
- Periodically check the installation for any signs of loosening or wear. This is necessary in mobile applications where constant vibration can loosen fittings.
Maintenance:
- Inspect the spring for signs of rust, corrosion, or mechanical wear. Rust can weaken the spring material, leading to failure, especially in outdoor environments.
- Clean the spring periodically to remove buildup of dirt, especially in outdoor environments. Dirt accumulation can cause wear and affect the spring's performance.
- Lubricate the spring if recommended by the manufacturer to ensure smooth operation and longevity. Not all springs require lubrication, so refer to the manufacturer's guidelines.
Safety Measures:
- Ensure that the spring and antenna assembly are kept away from electrical power lines to avoid potential hazards. Contact with power lines can lead to electrical shocks or damage to the equipment.
- Be cautious when driving under low-hanging obstacles if using mobile antenna springs to prevent damage to the vehicle and surroundings. For example, an extended antenna might catch on tree branches or low bridges, causing the spring to snap or damaging the antenna.
- Use appropriate safety gear, such as gloves, when handling and installing to avoid injury from sharp edges or broken components. Broken or rusted parts can cause cuts or puncture injuries if not handled correctly.
A Guide to Purchasing and Reviewing Antenna Springs
-
Determine Your Requirements:
- Assess where and how the antenna will be used. This helps in selecting the correct type of spring, such as heavy-duty for off-road use due to higher impacts or light-duty for urban driving with fewer structural challenges.
- Consider environmental factors like exposure to saltwater, extreme temperatures, or high wind conditions. For instance, saltwater environments may require materials resistant to corrosion.
-
Compare Materials and Build Quality:
- Choose antenna springs made of stainless steel for durability, as it is less prone to rust, extending the spring's functional life.
- Look for additional protective coatings if the antenna will be used in corrosive environments. These coatings provide extra protection against elements like salt and humidity.
-
Check Compatibility:
- Ensure the antenna spring is compatible with the antenna type and mounting hardware you have or plan to purchase. An incompatible spring may result in poor signal quality or physical instability.
- Review manufacturer specifications to ensure proper fit and function. Specifications often include details on weight capacity and mounting dimensions to ensure the spring can handle the intended load.
-
Read Customer Reviews:
- Look for feedback from other users who have installed the same spring in similar setups to understand its real-world performance. For example, if users in off-road scenarios report breakages, consider a different product.
- Pay attention to recurring issues mentioned in reviews, as these may indicate problems. Issues like premature rusting or weak connections are significant concerns.
-
Consider Brand Reputation:
- Choose antenna springs from brands known for reliability to ensure dependable performance. Established brands are more likely to offer consistent quality.
- Verify the warranty and customer support services provided by the manufacturer in case of defects or installation issues. A longer warranty period typically indicates higher confidence in the product's durability.
Conclusion
Antenna springs help protect antennas from damage and improve their performance. By knowing the different types, their specific uses, proper installation and maintenance, and the key factors to consider when purchasing, you can extend the lifespan and functionality of your antenna system. Choosing the right spring for your application and maintaining it correctly will lead to better communication and fewer equipment failures.