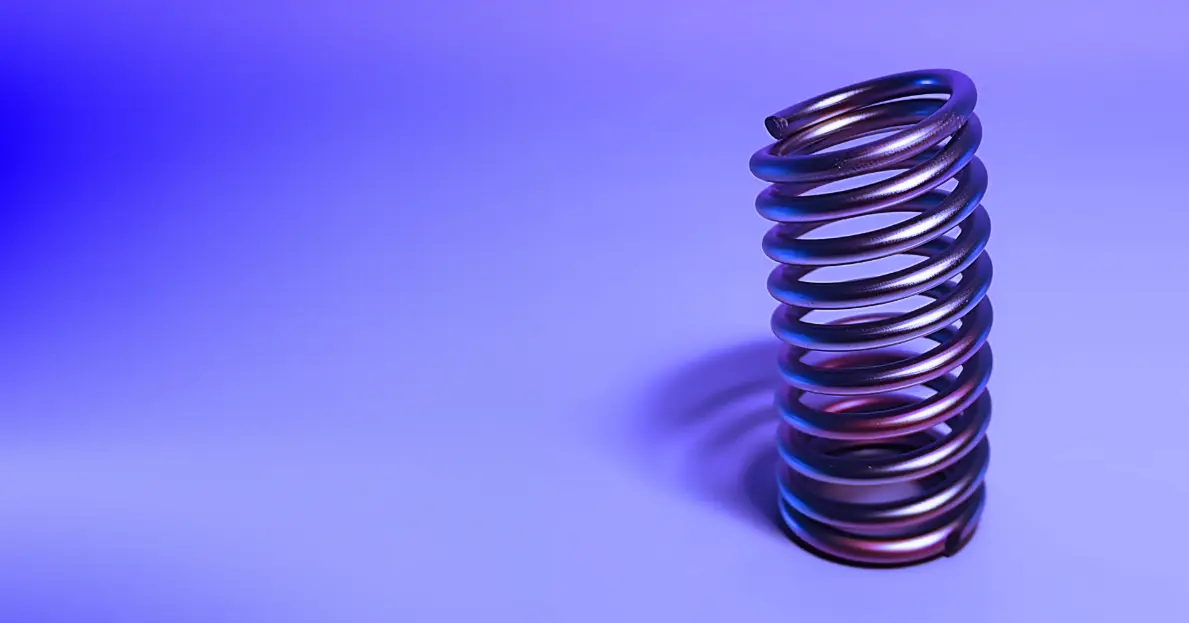
We're examining the differences between two prevalent types of springs in engineering: traditional coiled springs and machined springs. Understanding their characteristic features as well as their potential applications in various fields is crucial. An integral element in this comparison is also the manufacturing process of each spring type. As an example, a bridge might use machined springs for handling constant heavy loads, while a car's suspension system could use traditional coiled springs for better comfort and stability. We aim to equip you with comprehensive knowledge about both types of springs, aiding you in making informed decisions for your subsequent projects. Join us as we uncover the details.
Comparison of Machined Springs vs Traditional
Traditional coiled springs, also known as wound springs, are formed by winding wire around a cylinder. This manufacturing technique is typically less expensive and rapid, making it suited for numerous applications. However, the winding method can produce variable results, leading to differences in performance. For instance, in machines that require uniform behavior from all components, inconsistent performance of coiled springs could cause errors.
Conversely, machined springs are made from a single piece of solid material via processes such as drilling, cutting, and milling. These manufacturing steps enable enhanced control over the spring's characteristics, yielding a more stable outcome. Although the cost and production time are higher, machined springs are frequently used in sectors like aerospace where precise operation is required and unpredicted errors can lead to substantial problems.
When deciding between traditional coiled springs and machined springs, the specific needs of the application should guide the selection. Cost, the need for precision, and durability should be taken into consideration. Applications demanding high precision, such as aerospace systems, may benefit from the use of machined springs. Conversely, applications with budget constraints or where high precision is not a priority, might be better suited to traditional coiled springs due to their lower cost and faster production times.
Common Use Cases of Machined Springs
-
Heavy-duty machinery : Equipment designed for significant loads, such as hydraulic presses in manufacturing settings, use machined springs. These springs' mechanical properties allow for regular and safe management of the high forces in these machines.
-
Aerospace applications : The process used in the construction of these springs results in their prolonged lifespan and consistency. They are frequently selected for use within the aerospace sector. They can reliably manage the extreme environmental conditions, including high temperatures and pressures found in aerospace settings.
-
Medical equipment : In medical devices, such as MRIs, machined springs are a common choice due to their reliable performance characteristics. They contribute to precise movement within the machine's components, which is essential for accurate imaging results.
-
Automotive applications : Instances where optimal performance is required within vehicles often use machined springs. Although traditional coiled springs are commonly used within the automotive industry, machined springs are frequently chosen for systems with specific design requirements such as suspensions because of their lifespan and performance characteristics.
Machined Spring Manufacturers
-
Helical Products Company : This company produces high-precision machined springs. For example, their springs are used in aircraft navigation systems that require a high standard of precision and consistency.
-
Associated Spring : This manufacturer creates machined springs deployed in various applications, including automotive suspension systems. The springs used in this context need to exhibit durability and consistent performance, this explains the choice of Associated Spring's products.
-
Lee Spring : Their production is centered on making application-specific machined springs using current technology and modern manufacturing methods. A case in point is their production of springs for medical devices, taking into account both size precision and material safety. For general usage, the company's traditional coiled springs may be adequate and more economical.
Conclusion
Traditional coiled springs and machined springs each have distinct advantages and are chosen based on the specific needs of the use case. Coiled springs are often preferred for various applications due to their cost-effectiveness. On the other hand, machined springs may be more suitable when there is a demand for exactness, predictability, and long service life, such as in aerospace applications. Given this context, engineers can make informed decisions about the type of spring to incorporate into their designs. It is worth noting that the right spring can have a significant impact on projects in engineering fields such as automotive, medical, or heavy machinery. Therefore, careful spring selection is crucial.